【Phonetics】
Phonetics is the study of human speech sounds, how people utter the sounds and how the sounds are transmitted. And phonetics is the basis of linguistics because if sounds did not exist, any languages could not exist!
The spelling of English language is not equal to pronunciation, so there is a special way of representing it. The most famous transcription is International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). Based on this representation, people can learn how words are pronounced.
For example, phonetics are transcribed as / fənetɪks/.
The chart of transcription below shows IPA of consonants. This is a small version of this chart, so please click on the chart to see a full-size version.
(According to The International Phonetic Association
http://www.langsci.ucl.ac.uk/ipa/pulmonic.html)
And click HERE for another phonemic chart.
The chart of transcription below shows IPA of consonants. This is a small version of this chart, so please click on the chart to see a full-size version.
(According to The International Phonetic Association
http://www.langsci.ucl.ac.uk/ipa/pulmonic.html)
And click HERE for another phonemic chart.
[Question to consider]
If you click the bottom link, you will know the answer.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cJG0uErf8WY
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cJG0uErf8WY
Furthermore, phonetics has three main parts of study
(the following three points refer to THIS PAGE)
(the following three points refer to THIS PAGE)
・Articulatory phonetics
the study of how the vocal organs work when people produce speech sounds
the study of how the vocal organs work when people produce speech sounds

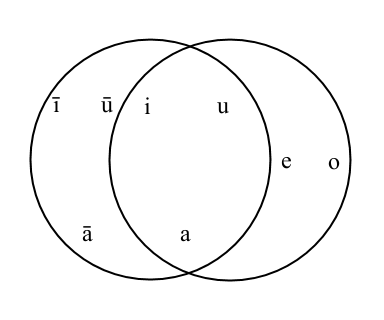
Speech sounds have two types of sounds, vowel and consonant. Vowels especially relate to the movements of tongue. There is a figure to show the relation between the place of tongue and vowel sounds, which is cited from The International Phonetic Association. It will help to pronounce vowels correctly.
・Acoustic phonetics
・Acoustic phonetics
the study of how the speech sounds travel in the air
Speech sounds are uttered from mouth and heard with ears. During the process, what happens? The sounds vibrate the air and it can be perceived. Sounds are invisible, so phoneticians or linguists use technical instruments and investigate it. The sound vibration appears as wave and it is different from high or low pitch and big or small volume.
・Auditory phonetics
the study of how people perceive speech sounds
There is only one way to recognize the sounds, which is hearing. The mechanism of hearing consists of many organs such as ear, brain and nerve. Researchers study how their ears work and how ears and brain are connected.
【Phonology】
Phonology is the study of the sound structure of languages, and how speech sounds are used to convey meaning.
Phonology is a part of linguistics.
How has man caught the sound?
Is calculation on what kind of phoneme performed in the brain?
How is phonological information stored in the brain?
What kind of system of grammar does it, put simply, have about the phoneme?
The segment is made of the feature which arises simultaneously, respectively.
Moreover, the flow of a speech is only expressed with the nonlinear model of phonology not as the sequence of the alignment of a sound segment but as a thing of many dimensions.
These nonlinear models are the phonology of an automatic division resulting from phonology with generative force, the phonology of measurement, the phonology of a vocabulary, etc.
Phonology is research on the sound and the speech pattern of language. The root "telephone" is related to sound in phonology, and begins from the word "phonema" of Greece which means sound. Its best is done in phonology to identify the sound made with all human beings' language. Discernment of an un-universal special feature is that sound is universal and a serious component of phonology as all the language use syllables and forms of a vowel and a consonant.
These nonlinear models are the phonology of an automatic division resulting from phonology with generative force, the phonology of measurement, the phonology of a vocabulary, etc.
Phonology is research on the sound and the speech pattern of language. The root "telephone" is related to sound in phonology, and begins from the word "phonema" of Greece which means sound. Its best is done in phonology to identify the sound made with all human beings' language. Discernment of an un-universal special feature is that sound is universal and a serious component of phonology as all the language use syllables and forms of a vowel and a consonant.
Phonology is the study of the sound structure of languages, and how speech sounds are used to convey meaning.
Syllables are a kind of unit to divide continuation speech sounds and unity of sound reception. There is only one vowel in one syllable except for diphthong, as "rain", "poor", "voice" and so on.
According to Cyprus, "Vowels allow air to escape from the mouth and nose unblocked, while consonants create more covering of the vocal tract by the tongue."
According to Cyprus, "Vowels allow air to escape from the mouth and nose unblocked, while consonants create more covering of the vocal tract by the tongue."
Phoneme is any one of the set of smallest units of speech in a language that distinguish one word from another(Oxford Dictionary 7th edition). When you change a syllable, the meaning of word changing syllable is changing. For example, "rise" and "rose" are same words except for syllables "i" and "o", however, their meanings are different.
If you want to understand more, please click here.
If you want to understand more, please click here.
[Question to consider]
Do you understand the difference between phonetics and phonology?If you cannot understand these characteristic, you click bottom link.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_69ATDAomLc
【Useful Links】
【Key Words】
・International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA): The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin alphabet. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association as a standardized representation of the sounds of spoken language. The IPA is used by foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech pathologists and therapists, singers, actors, lexicographers, artificial language enthusiasts (conlangers), and translators
・vocal organ: any of the organs involved in speech production
・vowel: a speech sound in which the mouth is open and the tongue is not
•consonant: a speech sound made by completely or partly stopping the flow of air being breathed out through the mouth
•phoneme: any one of the set of smallest units of speech in a language that distinguish one word from another
•syllable: any of the units into which a word is divided, containing a vowel sound and usually one or more consonants
•consonant: a speech sound made by completely or partly stopping the flow of air being breathed out through the mouth
•phoneme: any one of the set of smallest units of speech in a language that distinguish one word from another
•syllable: any of the units into which a word is divided, containing a vowel sound and usually one or more consonants
(Source of 5 words for Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. 7th ed.)
【Works Consulted】
Aitchison, Jean. Aitchison’s Linguistics. London: Teach Yourself, 2010.Print.
"Consonant." Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. 7th ed. 2005. Print.
“Consonants.” The International Phonetic Association. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.
Cyprus, Sheri. "What is Phonology?" wiseGEEK. n.d. Web. 14. Jan. 2014.
<http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-phonology.htm>
Gramley, Vivian. “Acoustic Phonetics.” Universitat Bielefeld. May 2010. Web. 18 October 2013.
"International Phonetic Alphabet." Wikipedia. n.d. Web. 14. Jan.2014.
Nordquist, Richard. “Phonetics- Grammar And Composition- About. Com.” About Com Grammar And Composition. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.
"Phoneme." Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. 7th ed. 2005. Print.
“Phonemic Chart.” English Club. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.
“Phonemic Chart.” English Club. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.
"Syllable." Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. 7th ed. 2005. Print.
“Vocal Organs Of Speech.” English, Baby! 6 October 2007. web. 18 October 2013.
"Vowel" Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. 7th ed. 2005. Print.
“Vowels.” The International Phonetic Association. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.
“Vowels.” The International Phonetic Association. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.
“What Is Phonetics?” All About Linguistics. The University Of Sheffield. n.d. web. 18 October 2013.



No comments:
Post a Comment